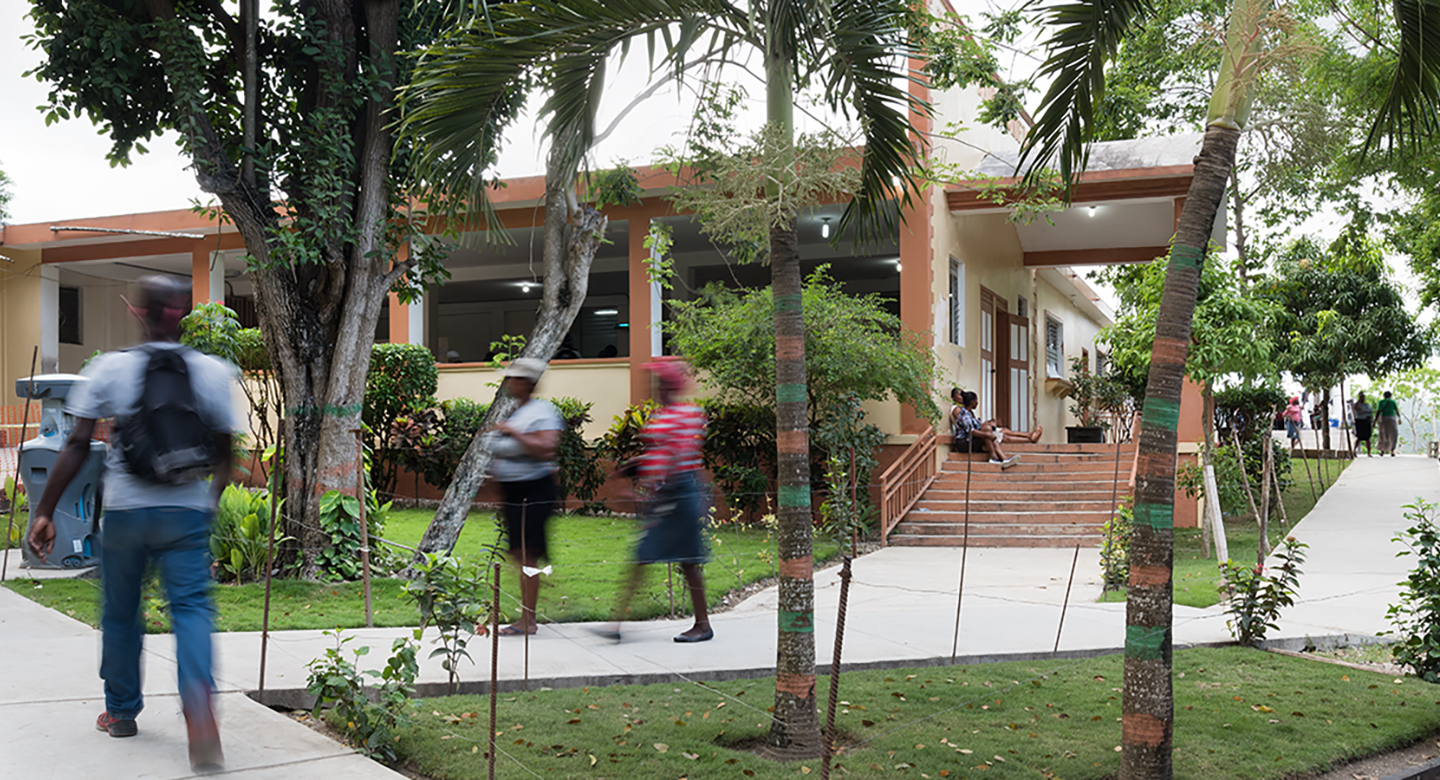


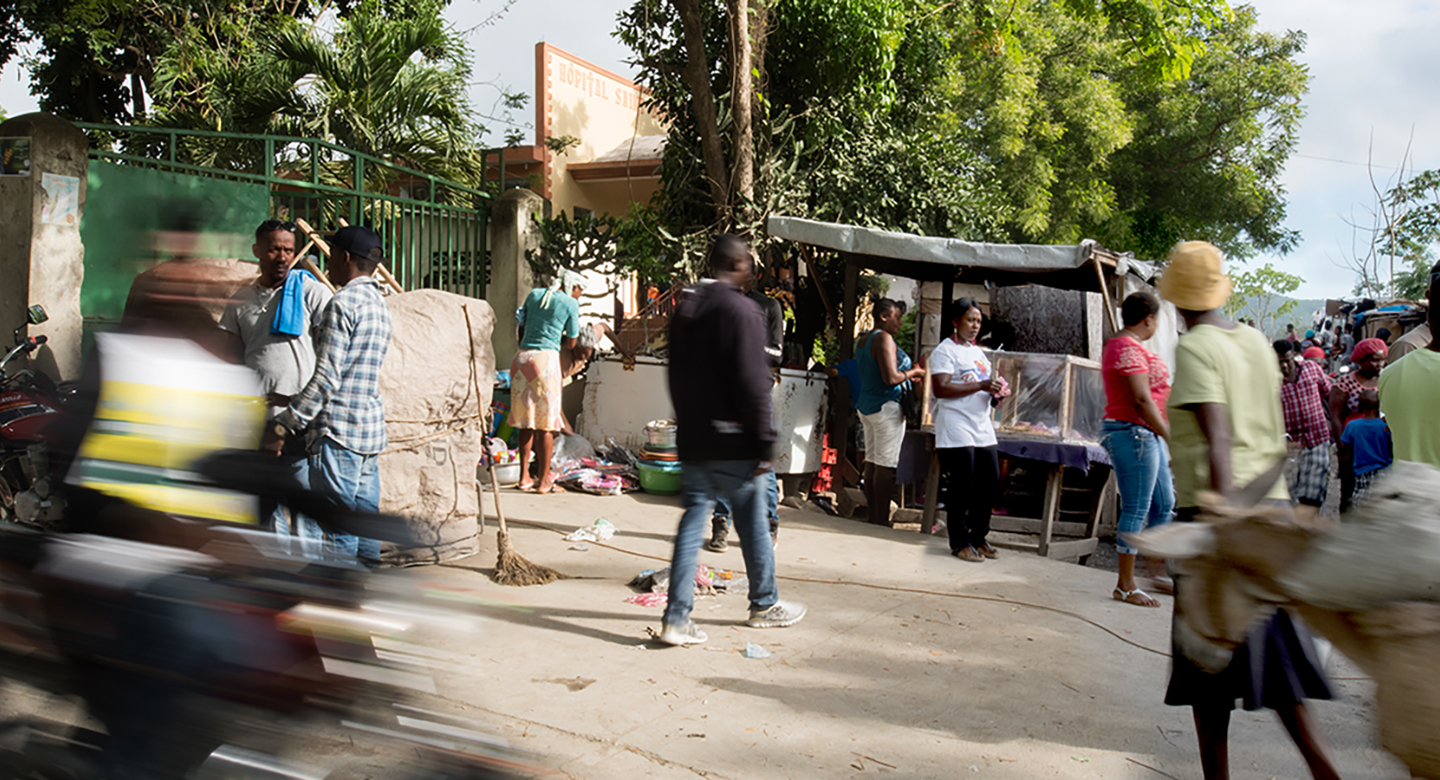
Saint Boniface Hospital (SBH), located in Fond des Blancs, Haiti, provides care to over 500 patients a day while battling systemic healthcare issues. Since its founding in 1992, the hospital has grown incrementally by expanding services and facilities to support the needs of the community. Today, SBH is the best equipped, and most developed hospital in the Southern Peninsula, but facing growing pains associated with its informal rapid growth. The exponential increase of daily patient visits and addition of new specialty services has emphasized the need for a master plan to help them maintain a high standard of care, improve the flow between services, relieve congestion, increase facility resilience, and create flexibility for planned future growth. The SBH Masterplan is a comprehensive planning document funded by W.K. Kellogg Foundation (WKKF), and compiled by Build Health International (BHI) on behalf of the SBH. The masterplan examines the current state of the hospital, the population health of the Fond des Blancs community, and the national health data. Through the examination of the existing conditions and factors affecting the hospital, its patients, staff and general catchment area, recommendations are made on how to grow and equip the hospital over the next five years to ensure improved patient outcomes. To keep the operational costs as low as possible, without compromising care, the Strategic Framework encourages strengthening the existing hospital programs by providing necessary upgrades to maximize efficiency. The masterplan outlines new facilities and systems that will aid in access to quality healthcare, and utilize sustainable design strategies while considering the impact on operational costs.
Saint Boniface Hospital / Health Equity
WKKF
Fond des Blancs, Haïti
January 2019
Healthcare
Masterplanning, Architecture
Build Health International, Project Fond-des-Blancs community, ADF, Jessica Rinaldi, Kat Kendon, Terry Sebastian
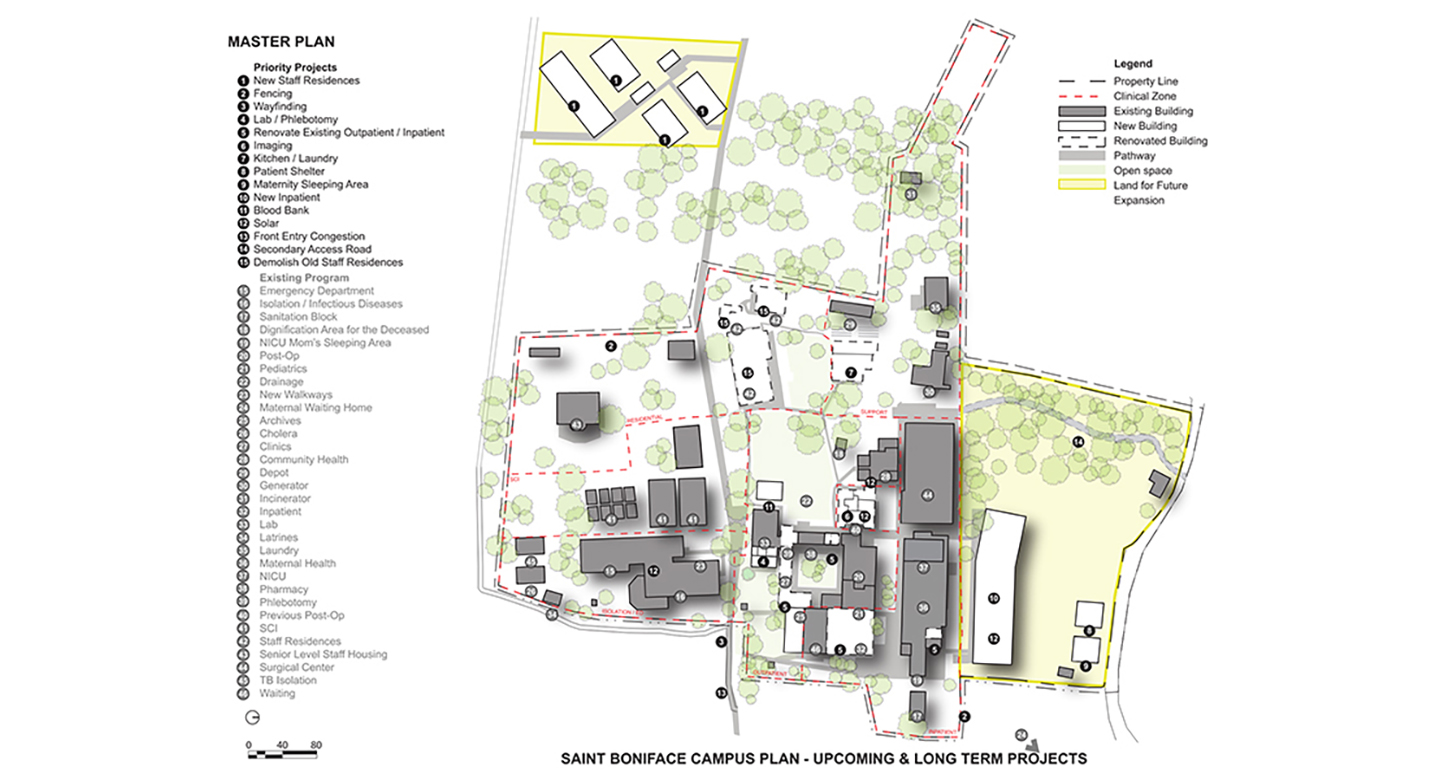
The SBH masterplan considers not only the capital costs of a project but the long-term operational costs. The plan is broken down into short-term and long-term projects so that the highest value add projects with low operational or capital costs associated with them are undertaken first. The larger projects can be completed when SBH determines that they have the funds to build as well as sustain. The masterplan design considers sub-phasing of projects as a means to always keep services operational throughout the project.
SBH priorities shifted throughout the planning process as a reaction to changing demands on the facility. To ensure we were incorporating their real-time feedback we detailed a project priority system for our weekly check-ins with the hospital team. Based on the current list of priorities the masterplan was updated and adjusted throughout the process. Each project was given a priority, a capital cost, and operations cost, timeframe, and impact overview. The project tracking system provides SBH with a holistic overview of their projects so they may continue to address their priorities ahead of undertaking a large capital project.
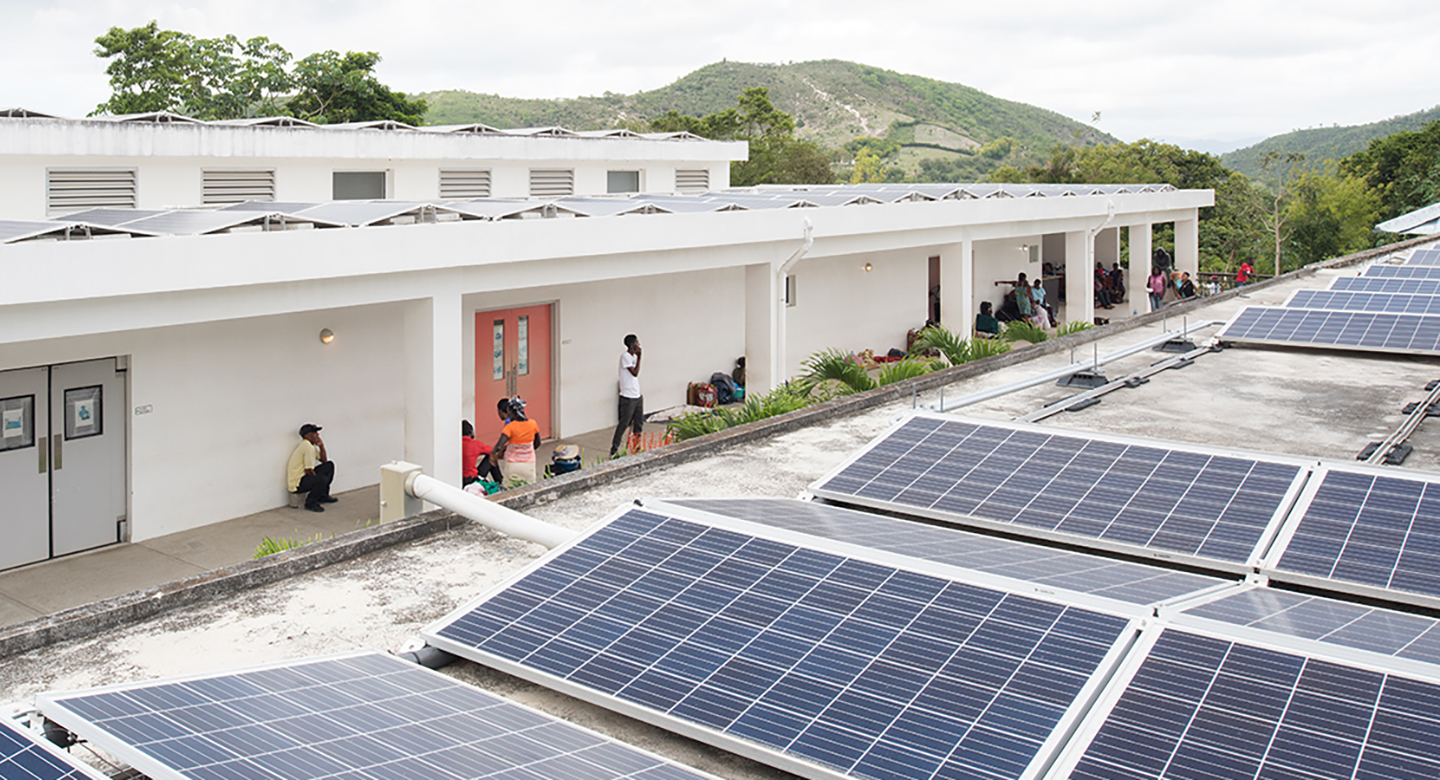
The masterplan places a high emphasis on long-term sustainability and ensures that any project undertaken will not adversely affect the operations of the campus. Sustainable systems and strategies are employed to minimize dependence on nonrenewable resources. The plan incorporates rainwater catchment, pit latrines, and improved stormwater management. The plan maps out the expansion of the existing solar grid to ensure the hospital operations can continue to function even when backup generators fail. Only spaces that critically require mechanical ventilation have AC units, all other spaces are passively cooled, with passive airflow as part of the design.
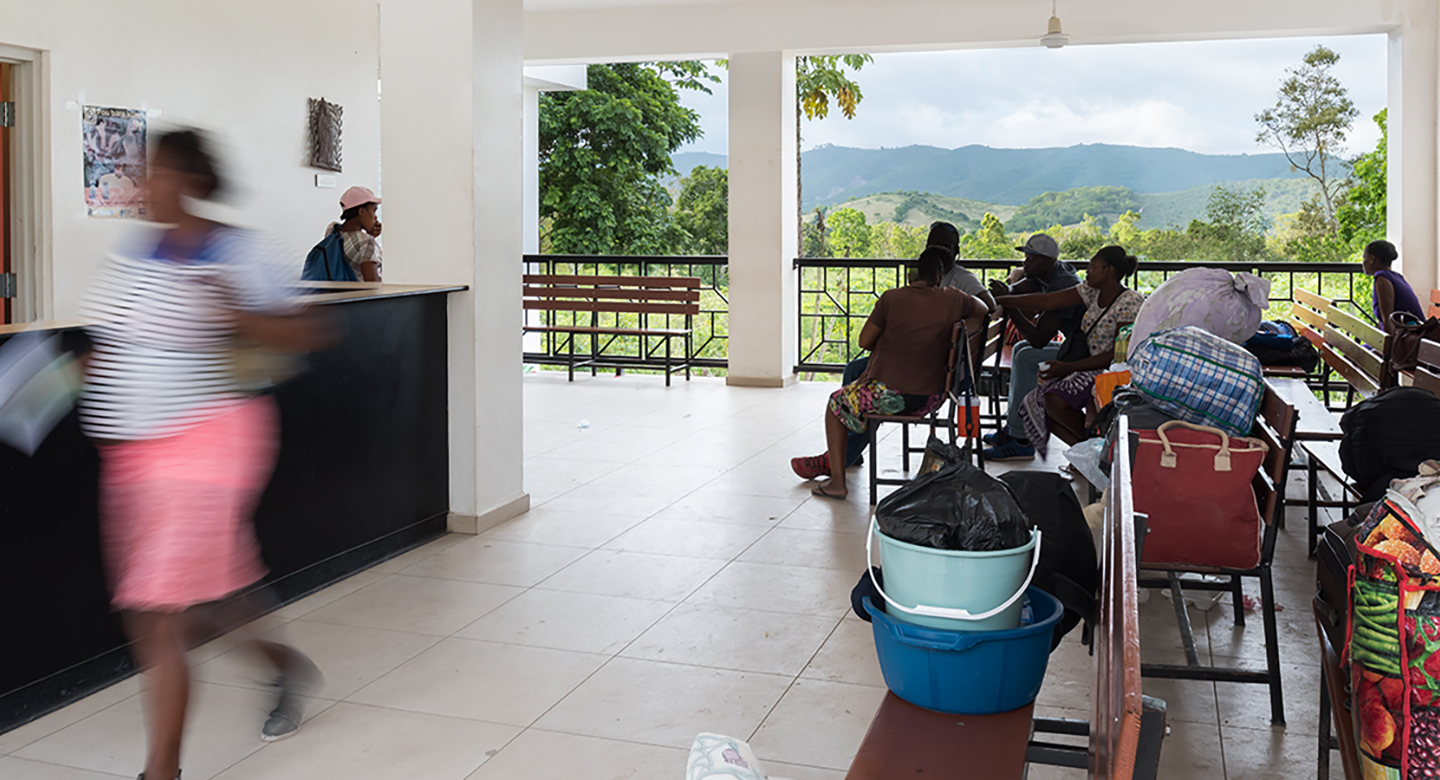
Short-term projects were completed in conjunction with the plan and address dignification of spaces, improved sanitation, improved quality of care, and accessibility of the campus. The long-term goals were set as action items to plan for in the coming years as they will require a larger capital cost and sustained operation costs. Long term projects include new staff residences, upgrading the campus security, incorporation of wayfinding, improvement of waiting spaces, renovation of clinical space, a central Radiology department, centralization of the campus kitchens and laundry, provide dignified shelter for overnight visitors, new inpatient facilities, and the expansion of the solar system.
GOAL 3: Good Health and Well-being
GOAL 5: Gender Equality
GOAL 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
GOAL 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
GOAL 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
GOAL 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure